Note
Click here to download the full example code
QPF (Laos)
This example demonstrates how to perform operational deterministic QPF up to three hours using reflectivity data.
Definitions
Import all required modules and methods:
# Python package to allow system command line functions
import os
# Python package to manage warning message
import warnings
# Python package for timestamp
import pandas as pd
# Python package for xarrays to read and handle netcdf data
import xarray as xr
# Python package for numerical calculations
import numpy as np
# Python com-swirls package to standardize attributes
from swirlspy.utils import standardize_attr, FrameType
# Python com-swirls package to calculate motion field (rover) and semi-lagrangian advection
from swirlspy.qpf import rover, sla
# directory constants
from swirlspy.tests.samples import DATA_DIR
from swirlspy.tests.outputs import OUTPUT_DIR
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# data files
data_paths = [
os.path.abspath(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'laos_h8/laos_20190731070000.nc')),
os.path.abspath(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'laos_h8/laos_20190731071000.nc')),
]
Initialising
This section demonstrates preprocessing reflectivity data.
# Read data from saved files
reflec_datas = []
for file_path in data_paths:
d = xr.open_dataarray(file_path)
reflec_datas.append(d)
# Concatenate list on time axis
data_frames = xr.concat(reflec_datas, dim='time')
# Make sure data is ordered by time
data_frames = data_frames.sortby('time', ascending=True)
Nowcast (SWIRLS-Radar-Advection)
The swirls radar advection was performed using the observed radar data Firstly, some attributes necessary for com-swirls input variable is added Secondly, rover function is invoked to compute the motion field Thirdly, semi-lagrangian advection is performed to advect the radar data using the rover motion field
# Adding in some attributes that is step_size <10 mins in pandas.Timedelta>, zero_value <numpy.nan> and frame_type <FrameType.dBZ>
standardize_attr(data_frames)
# Rover motion field computation
motion = rover(data_frames)
rover_time = pd.Timestamp.now()
# Semi-Lagrangian Advection
swirls = sla(data_frames, motion, 17) # Radar time goes from earliest to latest
RUNNING 'rover' FOR EXTRAPOLATION.....
Plotting result
Step 1: Import plotting library and necessary library
# Python package for reading map shape file
import cartopy.io.shapereader as shpreader
# Python package for land/sea features
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
# Python package for projection
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
# Python package for creating plots
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# Python package for output import grid
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
# Python package for colorbars
from matplotlib.colors import BoundaryNorm, ListedColormap
# Python package for scalar data to RGBA mapping
from matplotlib.cm import ScalarMappable
plt.switch_backend('agg')
Step 2: Defining the dBZ levels, colorbar parameters and projection
# levels of colorbar (dBZ)
levels = [-32768, 10, 15, 20, 24, 28, 32, 34, 38, 41, 44,
47, 50, 53, 56, 58, 60, 62]
# hko colormap for dBZ at each levels
cmap = ListedColormap([
'#FFFFFF00', '#08C5F5', '#0091F3', '#3898FF', '#008243', '#00A433',
'#00D100', '#01F508', '#77FF00', '#E0D100', '#FFDC01', '#EEB200',
'#F08100', '#F00101', '#E20200', '#B40466', '#ED02F0'
])
# boundary
norm = BoundaryNorm(levels, ncolors=cmap.N, clip=True)
# scalar data to RGBA mapping
scalar_map = ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
scalar_map.set_array([])
# Defining plot parameters
map_shape_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(
DATA_DIR,
'shape/se_asia'
))
# coastline and province
se_asia = cfeature.ShapelyFeature(
list(shpreader.Reader(map_shape_file).geometries()),
ccrs.PlateCarree()
)
# output area
extents = [99.5, 108., 13.75, 22.75]
# base_map plotting function
def plot_base(ax: plt.Axes):
ax.set_extent(extents, crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# fake the ocean color
ax.imshow(np.tile(np.array([[[178, 208, 254]]],
dtype=np.uint8), [2, 2, 1]),
origin='upper',
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
extent=[-180, 180, -180, 180],
zorder=-1)
# coastline, state, color
ax.add_feature(se_asia,
facecolor=cfeature.COLORS['land'], edgecolor='none', zorder=0)
# overlay coastline, state without color
ax.add_feature(se_asia, facecolor='none',
edgecolor='gray', linewidth=0.5)
ax.set_title('')
Step 3: Filtering values <= 15dbZ are not plotted
swirls = swirls.where(swirls > 15, np.nan)
# Defining motion quivers
qx = motion.coords['x'].values[::5]
qy = motion.coords['y'].values[::5]
qu = motion.values[0, ::5, ::5]
qv = motion.values[1, ::5, ::5]
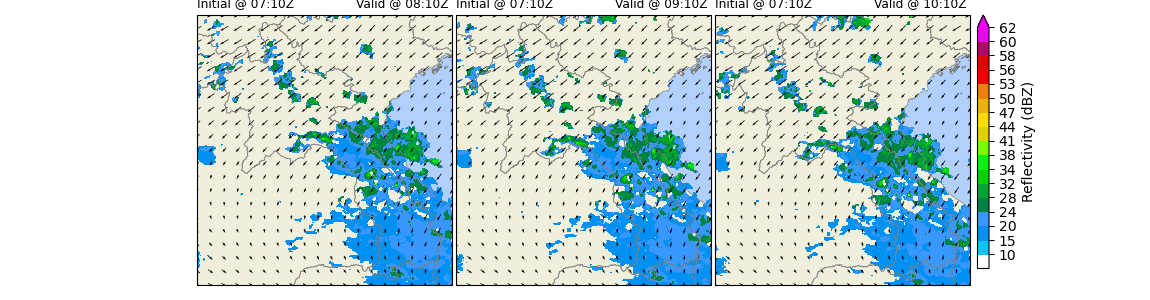
Step 4: Plotting the swirls-radar-advection, nwp-bias-corrected, blended 3 hours ahead
fig: plt.Figure = plt.figure(
figsize=(3 * 3.5 + 1, 3),
frameon=False
)
gs = GridSpec(
1, 3, figure=fig,
wspace=0, hspace=0, top=0.95, bottom=0.05, left=0.17, right=0.845
)
basetime = pd.Timestamp(swirls.time.values[0])
interval = pd.Timedelta(swirls.attrs['step_size'])
for col in range(3):
time_index = (col + 1) * 6 - 1
timelabel = basetime + pd.Timedelta(interval * (time_index + 1), 'm')
ax: plt.Axes = fig.add_subplot(
gs[0, col],
projection=ccrs.PlateCarree()
)
z = swirls[time_index].values
y = swirls[time_index].y
x = swirls[time_index].x
# plot base map
plot_base(ax)
# plot reflectivity
ax.contourf(
x, y, z, 60,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
cmap=cmap, norm=norm, levels=levels
)
# plot motion field
ax.quiver(qx, qy, qu, qv, pivot='mid', regrid_shape=20)
ax.set_title(
f"Nowcast\n" +
f"Initial @ {basetime.strftime('%H:%MZ')}",
loc='left', fontsize=8.75
)
ax.set_title('')
ax.set_title(
f"Initial {basetime.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')} \n" +
f"Valid @ {timelabel.strftime('%H:%MZ')} ",
loc='right', fontsize=8.75
)
cbar_ax = fig.add_axes([0.85, 0.105, 0.01, 0.845])
cbar = fig.colorbar(
scalar_map, cax=cbar_ax, ticks=levels[1:], extend='max', format='%.3g'
)
cbar.ax.set_ylabel('Reflectivity (dBZ)', rotation=90)
fig.savefig(
os.path.join(
OUTPUT_DIR,
"qpf_laos.png"
),
dpi=450,
bbox_inches="tight",
pad_inches=0.25
)
radar_image_time = pd.Timestamp.now()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 11.567 seconds)